News
Blog settimanale sulla Blockchain – Giugno 2024 #2 | Baker Hostetler

Annunciate le integrazioni TradFi/DeFi e il lancio di stablecoin a rendimento elevato
Secondo i rapporti, Robinhood, una delle principali società di servizi finanziari statunitensi, ha stipulato un accordo per acquisire Bitstamp, un exchange globale di criptovalute. Secondo un post sul blog di Bitstamp, Bitstamp ha uffici in Lussemburgo, Regno Unito, Slovenia, Singapore e Stati Uniti e detiene oltre 50 licenze e registrazioni attive a livello globale. Secondo quanto riferito, l’acquisizione accelererà la portata globale di Robinhood, farà crescere il suo business nel settore delle criptovalute e gli consentirà di servire clienti istituzionali.
Secondo un recente comunicato stampa, un’importante borsa statunitense sta collaborando con CoinDesk per lanciare opzioni su indici regolate in contanti che tracciano il CoinDesk Bitcoin Price Index (XBX). Il comunicato stampa rileva che le parti svilupperanno offerte di prodotti specifici in collaborazione con le autorità di regolamentazione. Il chief product officer della borsa ha dichiarato: “Dopo l’approvazione normativa, questi contratti di opzione offriranno agli investitori l’accesso a un importante strumento di gestione del rischio liquido e trasparente”.
Un altro recente comunicato stampa ha annunciato che l’affiliata di Paxos negli Emirati Arabi Uniti, una società di servizi finanziari e infrastrutture per asset digitali, ha lanciato USDL, definita la prima stablecoin a offrire ai detentori un rendimento giornaliero nei portafogli sotto controllo normativo. Secondo il comunicato stampa, l’entità emittente USDL è regolamentata dalla Financial Services Regulatory Authority (FSRA) del mercato globale di Abu Dhabi. Secondo quanto riferito, i detentori di USDL guadagneranno rendimento da titoli di stato statunitensi liquidi di alta qualità a breve termine e da attività di riserva equivalenti a liquidità detenute in conformità con le normative FSRA. Il rendimento verrà distribuito automaticamente agli indirizzi dei portafogli idonei.
Un terzo comunicato stampa ha annunciato che gli utenti dell’exchange di criptovalute sono ora in grado di inviare e ricevere criptovalute utilizzando le credenziali fornite da un’importante società di pagamenti statunitense “invece degli indirizzi blockchain solitamente lunghi e complessi”. Secondo il comunicato stampa, il sistema di credenziali aiuta a verificare le interazioni tra consumatori e aziende che utilizzano le reti blockchain.
Secondo i rapporti, un’altra importante società di pagamenti statunitense ha annunciato una partnership con Gnosis Pay, un fornitore di pagamenti decentralizzati, per consentire alle entità di collegare conti in criptovaluta alle carte di debito della società di pagamento. Queste carte di debito possono essere utilizzate per spendere criptovalute presso tutti i commercianti che accettano carte di debito emesse dalla società di pagamenti.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
Le zecche NFT continuano nonostante i dati indichino una flessione; Il caso di Dapper Labs si risolve
Secondo i rapporti, il mese scorso un importante produttore automobilistico europeo ha collaborato con Mojito, una piattaforma Web3 di coinvolgimento dei consumatori, per lanciare una nuova raccolta di token non fungibili (NFT). Secondo quanto riferito, la divisione Web3 della casa automobilistica ha venduto 780 NFT in una zecca aperta per sette giorni, dal 21 maggio al 28 maggio.
Tra le altre notizie sugli NFT, i dati pubblicati di recente indicano che il volume delle vendite globali di NFT è diminuito in modo significativo nel mese di maggio. Secondo i rapporti, le vendite globali di NFT a maggio sono state di 624 milioni di dollari, rispetto a oltre 1 miliardo di dollari di aprile, con un calo del 54%.
In un ultimo sviluppo degno di nota, la piattaforma NFT Dapper Labs avrebbe risolto un’azione legale collettiva con clienti che sostenevano che gli NFT Top Shot fossero titoli. Se l’accordo verrà approvato dal tribunale, la società pagherà 4 milioni di dollari ai querelanti della class action e i querelanti perderanno qualsiasi diritto futuro di rivendicare che gli NFT di Top Shot sono titoli.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
J5 pubblica indicatori di rischio per le attività crittografiche per le istituzioni finanziarie
Il 23 maggio, i Joint Chiefs of Global Tax Enforcement (J5) hanno rilasciato una nota consultiva alle istituzioni finanziarie evidenziando cinque indicatori di rischio legati agli asset in criptovaluta che potrebbero essere indicativi di riciclaggio di denaro, criminalità informatica, evasione fiscale e altre attività illecite. Di seguito una breve descrizione dei cinque indicatori di rischio:
- Stratificazione delle risorse crittografiche. Gli indicatori includono un rapido movimento di fondi tra conti senza alcuna logica aziendale apparente; inviare/ricevere transazioni maggiori del previsto da portafogli privati; conversione ad alto volume/frequenza di fondi su più asset crittografici; transazioni ad alto volume con piattaforme peer-to-peer (P2P); transazioni con mixer, piattaforme di gioco d’azzardo, mercati della darknet, negozi fraudolenti o scambi ad alto rischio; grande attività con privacy coin; e le transazioni che fluiscono attraverso più indirizzi in breve tempo appena prima di essere depositate o subito dopo essere ritirate dal portafoglio di un cliente.
- Rischio geografico. Gli indicatori includono transazioni con borse valori in giurisdizioni ad alto rischio; modifica degli indirizzi IP; Indirizzi IP in giurisdizioni ad alto rischio; e rapporti con chiavi pubbliche crittografiche presenti in elenchi di controllo come l’elenco dei cittadini appositamente designati dall’Office of Foreign Assets Control.
- Controparti ad alto rischio. Gli indicatori includono asset crittografici provenienti da sportelli OTC che pubblicizzano la privacy; invio/ricezione diretta di fondi da scambi di criptovalute in giurisdizioni ad alto rischio; e interazione con chiavi pubbliche con collegamenti a fonti sospette note.
- Onboarding di nuovi clienti. Gli indicatori includono la fornitura di informazioni di identificazione incomplete; difficoltà nell’accertare la titolarità effettiva o nel contattare il cliente; attività transazionale non coerente con il profilo del cliente; più clienti che si registrano in un breve periodo utilizzando indicatori di identità condivisi; utilizzo di indirizzi e-mail/provider orientati all’anonimato; utilizzo di indirizzi crittografici legati ad attività illecite o indagini pubbliche; accesso a più criptovalute o conti bancari; modifiche multiple alle informazioni sull’account; indirizzi email collegati a piattaforme crittografiche P2P; conti in paesi diversi da quello di nazionalità/residenza; e riluttanza a fornire informazioni sulla fonte dei fondi o sull’utilizzo delle monete private.
- Ransomware e crimini informatici. Gli indicatori includono un uso insolito o elevato di privacy coin; salto di catena; miscelatori; conti mulo; trasferimenti di grandi volumi seguiti da poche o nessuna ulteriore attività; conti crittografici collegati a più conti bancari presso diversi istituti finanziari; e nuovi clienti che effettuano acquisti immediati di grandi dimensioni in criptovalute seguiti da ritiro immediato a un indirizzo esterno.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
Il DFS di New York pubblica una guida al servizio clienti per le aziende cripto
Il Dipartimento dei servizi finanziari di New York (NY DFS) ha recentemente pubblicato una guida per le entità di valuta virtuale (VCE) autorizzate nello Stato di New York in merito alle richieste e ai reclami del servizio clienti. Secondo la guida, l’esperienza del NY DFS “indica che le politiche e le procedure di un VCE in merito alle richieste e ai reclami del servizio clienti difficilmente saranno sufficienti a meno che non affrontino efficacemente i problemi e incorporino i meccanismi delineati” nella guida. La guida affronta i concetti che dovrebbero essere presenti nelle politiche e nelle procedure di un VCE relative a (1) comunicazioni telefoniche ed elettroniche di testo; (2) fornire informazioni tempestive, sufficientemente dettagliate e accurate ai clienti; (3) fornire domande frequenti relative ai problemi del servizio clienti; (4) monitoraggio e garanzia della qualità; e (5) riferire al NY DFS sulle richieste e sui reclami del servizio clienti.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
Le azioni di applicazione del DOJ mirano agli schemi di riciclaggio di denaro crittografico
Il Dipartimento di Giustizia degli Stati Uniti (DOJ) ha recentemente pubblicato un comunicato stampa in cui annuncia che due cittadini estoni sono stati estradati negli Stati Uniti “per affrontare accuse penali legate al loro ruolo in un massiccio schema Ponzi di criptovaluta dalle molteplici sfaccettature”. Secondo il comunicato stampa, gli imputati “avrebbero indotto centinaia di migliaia di vittime ad acquistare contratti che davano loro diritto a una quota di valuta virtuale estratta dal presunto servizio di mining di criptovaluta degli imputati, HashFlare” a pagamento. Gli imputati avrebbero stipulato tali contratti per un valore di oltre 550 milioni di dollari. Tuttavia, “HashFlare presumibilmente non aveva l’attrezzatura per il mining di valuta virtuale che dichiarava di avere”, “era impegnata in meno dell’1% dell’attività di mining di Bitcoin dichiarata” e “non poteva pagare gli investitori con la valuta minata che avevano promesso”.
Inoltre, gli imputati presumibilmente “hanno offerto investimenti in una società chiamata Polybius, che secondo loro avrebbe formato una banca specializzata in valuta virtuale” e “hanno promesso di pagare agli investitori i dividendi dai profitti di Polybius”. Secondo il comunicato stampa gli imputati non hanno mai costituito una banca e non hanno mai pagato dividendi. Invece, gli imputati “hanno raccolto almeno 25 milioni di dollari e utilizzato circa 7 milioni di dollari dei proventi di HashFlare in questo schema e presumibilmente hanno trasferito la maggior parte del denaro su altri conti bancari e portafogli di valuta virtuale controllati da loro e dai loro cospiratori”. Secondo il comunicato stampa, gli imputati “avrebbero utilizzato società di comodo e contratti e fatture fasulli per riciclare i proventi della frode e per acquistare beni immobili e auto di lusso” in uno schema che “ha coinvolto almeno 75 proprietà immobiliari, sei veicoli di lusso, portafogli di criptovaluta e migliaia di macchine per il mining di criptovalute.”
Un altro recente comunicato stampa del Dipartimento di Giustizia ha annunciato l’apertura di un atto d’accusa che accusa “il direttore finanziario di una società multinazionale di media con sede a New York City di aver partecipato a un programma transnazionale per riciclare almeno circa 67 milioni di dollari di fondi ottenuti illegalmente a beneficio suo e dei media”. azienda.” Tra le altre cose, il comunicato stampa sottolineava che lo schema prevedeva l’utilizzo di “criptovaluta per acquistare consapevolmente decine di milioni di dollari in proventi criminali, compresi i proventi di indennità di disoccupazione ottenute in modo fraudolento, che erano stati caricati su decine di migliaia di carte di debito prepagate”. Secondo il comunicato stampa, i proventi del reato sarebbero stati acquistati “utilizzando una particolare piattaforma di criptovaluta, a tassi scontati di circa 70-80 centesimi per dollaro, e in cambio di criptovaluta”.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
Borsa giapponese violata per 305 milioni di dollari; Nuovi dati rilasciati sugli hack crittografici del 2024
Secondo recenti rapporti, l’exchange di criptovalute giapponese DMM Bitcoin ha perso 4.502,9 BTC (circa 305 milioni di dollari) in un hack. Secondo quanto riferito, questo è il secondo hack di criptovaluta più grande in Giappone dopo l’hacking del 2018 dell’exchange Coincheck per criptovaluta del valore di 58 miliardi di yen (circa 370 milioni di dollari).
Un rapporto recentemente pubblicato da Immunefi fornisce nuovi dati sulle perdite dovute ad attacchi informatici, truffe e altri exploit di criptovaluta. I risultati del rapporto includono quanto segue:
- A partire da maggio 2024, 473.229.944 dollari sono stati persi a causa di hack e furti di tappeti nell’anno in corso nel 2024 in 108 incidenti specifici, che rappresentano una diminuzione del 20% rispetto allo stesso periodo del 2023.
- Nel maggio 2024, 52.371.900 dollari sono stati persi a causa di attacchi informatici e frodi in 21 incidenti specifici, con una diminuzione del 12% rispetto a maggio 2023.
- La maggior parte delle perdite di maggio 2024 sono attribuibili agli exploit del progetto di gioco di criptovaluta Gala Games (21 milioni di dollari) e del protocollo DeFi SonneFinance (20 milioni di dollari).
- Nel maggio 2024, la DeFi è stata l’obiettivo principale degli exploit, mentre la CeFi non ha subito un solo attacco importante.
- Nel maggio 2024, sono andati persi complessivamente 50.618.600 dollari a causa di attacchi hacker in 14 incidenti specifici, mentre 1.753.300 dollari sono andati persi a causa di frodi in sette incidenti specifici.
Per ulteriori informazioni si rimanda ai seguenti link:
Avviso: legislazione sulle risorse digitali: è improbabile che l’approvazione alla Camera di FIT21 abbia slancio al Senato
La Camera ha approvato la HR 4763, la Legge sull’innovazione e la tecnologia finanziaria per il 21° secolo (FIT21)., con un voto di 279-136, di cui 71 voti dei democratici. Il disegno di legge è stato approvato nonostante l’opposizione della Casa Bianca in a Dichiarazione di politica amministrativa e opposizione in a dichiarazione del presidente della Securities and Exchange Commission statunitense Gary Gensler. Brevi descrizioni del disegno di legge possono essere trovate nel nostro recente post sul blog e nel comunicato stampa dalla commissione per i servizi finanziari della Camera che annuncia l’approvazione del disegno di legge.
[View source.]
News
Terra Can’t Catch a Break as Blockchain Gets $6 Million Exploited

The attack, which exploited a vulnerability disclosed in April, drained around 60 million ASTRO tokens, sending the price plummeting.
The Terra blockchain has been exploited for over $6 million, forcing developers to take a momentary break the chain.
Beosin Cyber Security Company reported that the protocol lost 60 million ASTRO tokens, 3.5 million USDC, 500,000 USDT, and 2.7 BTC or $180,000.
Terra developers paused the chain on Wednesday morning to apply an emergency patch that would address the attack. Moments later, a 67% majority of validators upgraded their nodes and resumed block production.
The ASTRO token has plunged as much as 75%. It is now trading at $0.03, a 25% decline on the day. Traders who took advantage of the drop are now on 195%.
The vulnerability that took down the Cosmos-based blockchain was disclosed in April and involved the deployment of a malicious CosmWasm contract. It opened the door to attacks via what is called an “ibc-hooks callback timeout reentrancy vulnerability,” which is used to invoke contracts and enable cross-chain swaps.
Terra 2.0 also suffered a massive drop in total value locked (TVL) in April, shortly after the vulnerability was discovered. It plunged 80% to $6 million from $30 million in TVL and has since lost nearly half of that value, currently sitting at $3.9 million.
The current Earth chain emerged from the rubble as a hard fork after the original blockchain, now called Terra Classic, collapsed in 2022. Terra collapsed after its algorithmic stablecoin (UST) lost its peg, causing a run on deposits. More than $50 billion of UST’s market cap was wiped out in a matter of days.
Terraform Labs, the company behind the blockchain, has been slowly unravelling its legal woes since its mid-2022 crash. Founder Do Kwon awaits sentencing in Montenegro after he and his company were found liable for $40 billion in customer funds in early April.
On June 12, Terraform Labs settled with the SEC for $4.4 billion, for which the company will pay about $3.59 billion plus interest and a $420 million penalty. Meanwhile, Kwon will pay $204.3 million, including $110 million in restitution, interest and an $80 million penalty, a court filing showed.
News
Google and Coinbase Veterans Raise $5M to Build Icebreaker, Blockchain’s Answer to LinkedIn
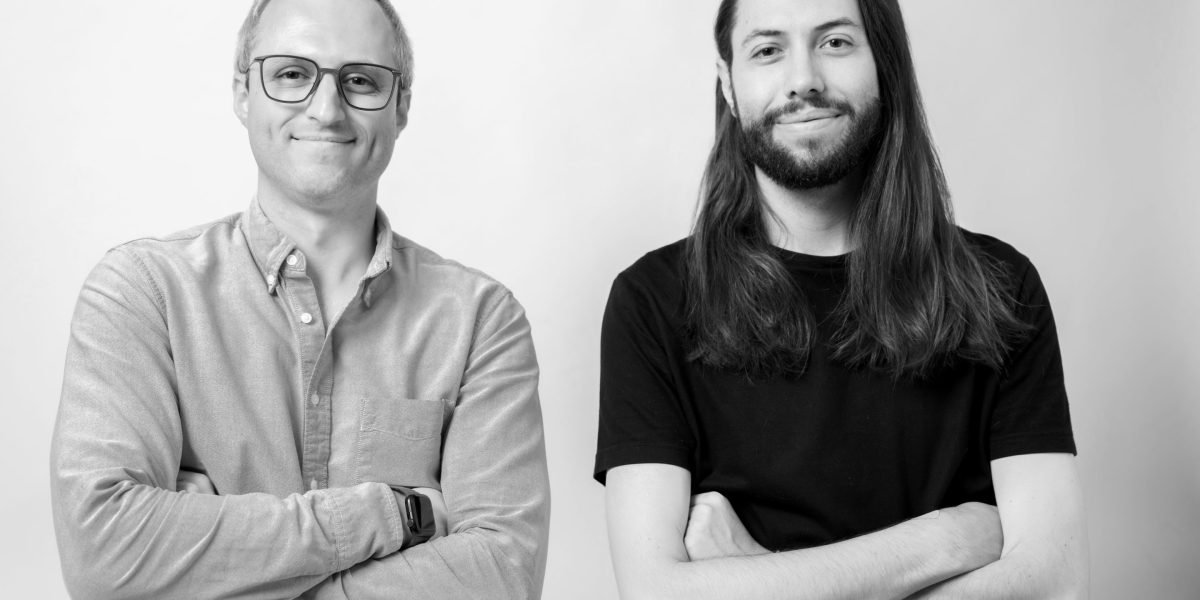

Icebreaker: Think LinkedIn but on a Blockchain—announced Wednesday that it has secured $5 million in seed funding. CoinFund led the round, with participation from Accomplice, Anagram, and Legion Capital, among others.
The company, which is valued at $21 million, aims to become the world’s first open-source network for professional connections. Its co-founders, Dan Stone and Jack Dillé, come from Google AND Monetary base; Stone was a product manager at the cryptocurrency giant and also the co-creator of Google’s largest multi-identity measurement and marketing platform, while Dillé was a design manager for Google Working area.
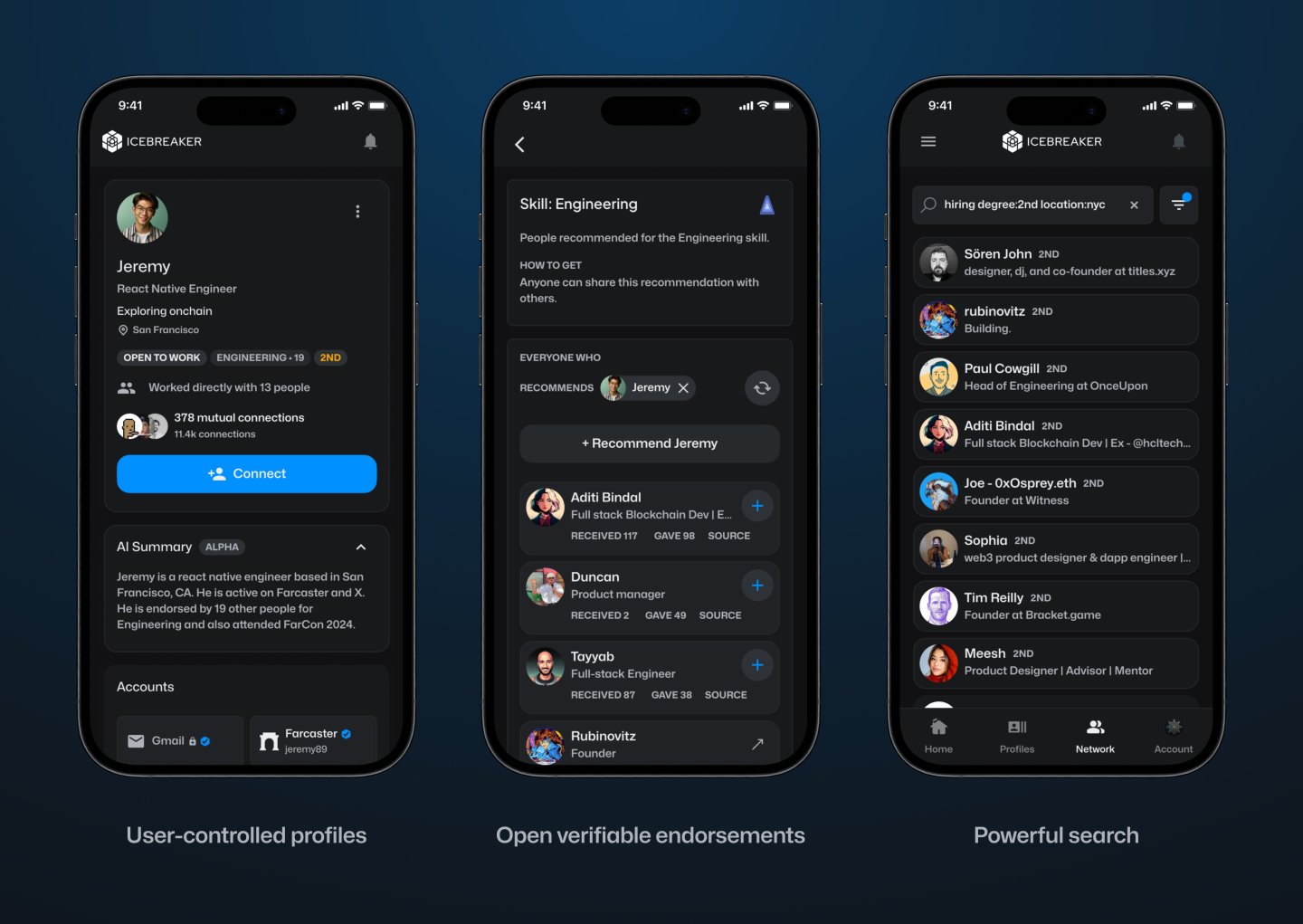
The pair founded Icebreaker on the shared belief that the imprint of one’s digital identity (and reputation) should not be owned by a single entity, but rather publicly owned and accessible to all. Frustrated that platforms like LinkedIn To limit how we leverage our connections, Dillé told Fortune he hopes to remove paywalls and credits, which “force us to pay just to browse our network.” Using blockchain technology, Icebreaker lets users transfer their existing professional profile and network into a single, verified channel.
“Imagine clicking the login button and then seeing your entire network on LinkedIn, ChirpingFarcaster and email? Imagine how many introductions could be routed more effectively if you could see the full picture of how you’re connected to someone,” Stone told Fortune.
Users can instantly prove their credentials and provide verifiable endorsements for people in their network. The idea is to create an “open graph of reputation and identity,” according to the founders. They hope to challenge LinkedIn’s closed network that “secures data,” freeing users to search for candidates and opportunities wherever they are online. By building on-chain, the founders note, they will create a public ledger of shared context and trust.
Verified channels are now launched for
Chirping
Online Guide
Wallet
Discord
Telephone
TeleporterYou can find them in Account -> Linked Accounts Italian: https://t.co/mRDyuWW8O2
— Icebreaker (@icebreaker_xyz) April 3, 2024
“Digital networking is increasingly saturated with noise and AI-driven fake personas,” the founders said in a statement. For example: Dillé’s LinkedIn headline reads “CEO of Google,” a small piece of digital performance art to draw attention to unverifiable information on Web2 social networks that can leave both candidates and recruiters vulnerable to false claims.
“Icebreaker was created to enable professionals to seamlessly tap into their existing profiles and networks to surface exceptional people and opportunities, using recent advances in cryptographically verifiable identity,” the company said, adding that the new funding will go towards expanding its team and developing products.
“One of the next significant use cases for cryptocurrency is the development of fundamental social graphs for applications to leverage… We are proud to support Dan, Jack and their team in their mission to bring true professional identity ownership to everyone online,” said CoinFund CIO Alex Felix in a statement.
Learn more about all things cryptocurrency with short, easy-to-read flashcards. Click here to Fortune’s Crash Course in Cryptocurrency.
Fuente
News
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
News
New bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work

The Department of Veterans Affairs would have to evaluate how blockchain technology could be used to improve benefits and services offered to veterans, according to a legislative proposal introduced Tuesday.
The bill, sponsored by Rep. Nancy Mace, R-S.C., would direct the VA to “conduct a comprehensive study of the feasibility, potential benefits, and risks associated with using distributed ledger technology in various programs and services.”
Distributed ledger technology, including blockchain, is used to protect and track information by storing data across multiple computers and keeping a record of its use.
According to the text of the legislation, which Mace’s office shared exclusively with Nextgov/FCW ahead of its publication, blockchain “could significantly improve benefits allocation, insurance program management, and recordkeeping within the Department of Veterans Affairs.”
“We need to bring the federal government into the 21st century,” Mace said in a statement. “This bill will open the door to research on improving outdated systems that fail our veterans because we owe it to them to use every tool at our disposal to improve their lives.”
Within one year of the law taking effect, the Department of Veterans Affairs will be required to submit a report to the House and Senate Veterans Affairs committees detailing its findings, as well as the benefits and risks identified in using the technology.
The mandatory review is expected to include information on how the department’s use of blockchain could improve the way benefits decisions are administered, improve the management and security of veterans’ personal data, streamline the insurance claims process, and “increase transparency and accountability in service delivery.”
The Department of Veterans Affairs has been studying the potential benefits of using distributed ledger technology, with the department emission a request for information in November 2021 seeking input from contractors on how blockchain could be leveraged, in part, to streamline its supply chains and “secure data sharing between institutions.”
The VA’s National Institute of Artificial Intelligence has also valued the use of blockchain, with three of the use cases tested during the 2021 AI tech sprint focused on examining its capabilities.
Mace previously introduced a May bill that would direct Customs and Border Protection to create a public blockchain platform to store and share data collected at U.S. borders.
Lawmakers also proposed additional measures that would push the Department of Veterans Affairs to consider adopting other modernized technologies to improve veteran services.
Rep. David Valadao, R-Calif., introduced legislation in June that would have directed the department to report to lawmakers on how it plans to expand the use of “certain automation tools” to process veterans’ claims. The House of Representatives Subcommittee on Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs gave a favorable hearing on the congressman’s bill during a Markup of July 23.
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin, ETH Price, CPI Print, PYTH, WIF & MORE!!
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin Price, ETF, ETH, WIF, HNT & MORE!!
-

 DeFi9 months ago
DeFi9 months agoMetasphere Labs announces follow-up event regarding
-
 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoSolana price potential?! Check out THIS update if you own SOL!!
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoWho Really CONTROLS THE MARKETS!! Her plans REVEALED!!
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoPump.Fun Overtakes Ethereum in Daily Revenue: A New Leader in DeFi
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoDegens Can Now Create Memecoins From Tweets
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoNew bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoLawmakers, regulators to study impact of blockchain and cryptocurrency in Alabama • Alabama Reflector
-

 Bitcoin6 months ago
Bitcoin6 months ago1 Top Cryptocurrency That Could Surge Over 4,300%, According to This Wall Street Firm
-

 Ethereum8 months ago
Ethereum8 months agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoCryptocurrency News: BTC Rally, ETH, SOL, FTM, USDT Recover & MORE!

 ASTRO Price
ASTRO Price



