News
Blockchain Tutorial for Beginners [Updated 2024]

Topics Covered
- What is Blockchain Technology?
- Features of Blockchain?
- Why is Blockchain Important?
- What Is Cryptocurrency?
- What is a Blockchain Wallet?
- What is Ethereum?
- Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which One is Better?
- What is Ethereum Mining?
- What is a Smart Contract in Blockchain?
- What is Dogecoin?
- Dogecoin vs. Bitcoin
- Dogecoin Mining: Understanding The Fundamentals
- A Look into The Digital Dogecoin Wallet
- 5 Industries That Blockchain Will Disrupt in Future
- Emerging Blockchain Applications Across Industries
- How To Become a Blockchain Developer?
- What is NFT?
- The complete guide on Solidity Programming
- The Future of Shiba Inu Coin
- Understanding the Fundamentals of Ethereum Classic
- What is the Merkle Tree in Blockchain?
- What is Cardano?
- What is Matic Network?
- Top 30 Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers for 2022
- What is Tether?
- A Comprehensive Comparison Of NFT Vs. Crypto
- What Is Web 3.0?
- Types of Blockchain
- What Is DeFi?
- What Is Ripple?
- What Is Binance?
Accelerate Your Full Stack Development Career!
Full Stack Java DeveloperExplore Program![]()
Blockchain Tutorial: Table of Contents
Lesson 1: What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a new way of handling digital transactions that have started to gain traction in recent years. It works by creating an unalterable record of all the transactions that have ever taken place on a network called a blockchain. This means that no one can tamper with or edit the records without being detected and punished.
Lesson 2: Features Of Blockchain
Blockchain is a new technology that is changing the way we do business. Originally designed as a way to remove the need for a middleman in transactions, it has since been used for a variety of purposes, including but not limited to identity management, supply chain management, and data storage.
Lesson 3: Why Blockchain Is Important?
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. This technology has the potential to change the way we do business and could even have far-reaching implications for society as a whole. Here are four reasons why blockchain is so important:
- Blockchain is secure
- Blockchain is transparent
- Blockchain is tamper-proof
- Blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions without reliance on a central authority or third parties like banks
Lesson 4: What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to encrypt its transactions and regulate the creation of new units. They are often traded on decentralized exchanges and can also be used to purchase goods and services.
Lesson 5: What Is A Blockchain Wallet?
A blockchain wallet is a digital wallet that allows you to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and Ethereum. Blockchain wallets are similar to traditional bank accounts in that they allow users to easily transfer funds between their various accounts. But where banks rely on centralized systems to hold customers’ money, blockchain wallets use decentralized technology to manage transactions.
Lesson 6: What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that runs smart contracts: applications that run exactly as programmed without any possibility of fraud or third-party interference. It’s this unique feature that makes Ethereum especially appealing to developers and entrepreneurs, who can use it to build apps on top of it with no risk of censorship or theft.
Learn Through Industry-relevant Projects!
Caltech Blockchain BootcampExplore Program![]()
Lesson 7: Bitcoin vs Ethereum: Which One is Better?
- Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries. Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public dispersed ledger called a blockchain.
- Ethereum is also a decentralized digital currency, but it goes beyond being just a payment system. It is also a platform that allows developers to build and run decentralized applications (dapps). These dapps can be used to create anything from smart contracts to Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
Lesson 8: What Is Ethereum Mining?
Ethereum Mining is the process of using your computer to help power the Ethereum network and reward participants for their contributions. Every time a user sends a transaction on the Ethereum network, they are rewarded with Ether (ETH). This helps keep the network running and protected from malicious attacks.
Lesson 9: What Is A Smart Contract in Blockchain?
A Smart Contract is a contract that is executed through the use of blockchain technology. This involves a digital ledger of all contracts and transactions, which are tamper-proof and accessible by everyone on the network. Whenever someone tries to modify or delete a contract, their attempt will be recorded in the public ledger as well. This makes it difficult for anyone to falsify records or try to cheat other participants.
Lesson 10: What Is Dogecoin?
Dogecoin is a cryptocurrency that was created as a fun way to make online transactions more accessible. It started as an imitation of Bitcoin, but it has since developed its unique properties and currency system. Dogecoin uses a peer-to-peer network to facilitate transactions. Unlike many other cryptocurrencies, Dogecoin has a very easy-to-use blockchain, making it a popular choice for new cryptocurrency users.
Lesson 11: Dogecoin vs. Bitcoin
Dogecoin and Bitcoin are both types of digital currencies. But what’s the difference between them?
- Bitcoin is more popular than Dogecoin
- Bitcoin offers greater potential for growth than Dogecoin does currently.
- Dogecoin has an active community of supporters who give it extra liquidity and push its prices up during volatile markets.
- Bitcoin is more centralized than Dogecoin – mining pools control about 50% of all hashing power on the network, while Dogecoin relies on users distributed across the web to contribute their computing resources. This creates more stability for Doges overall because individuals cannot corrupt or cheat the system easily as they can with Bitcoin.
Lesson 12: What is Dogecoin Mining?
Dogecoin mining is the process of using a computer to validate and add new transactions to the Dogecoin blockchain. Mining Dogecoin can be a fun way to earn some extra money, and it also helps support the development of the cryptocurrency. Miners are rewarded with Dogecoins for their participation in this process.
Kickstart Your MERN Stack Career With Us!
Full Stack Developer – MERN StackExplore Program![]()
Lesson 13: Digital Dogecoin Wallet
A digital Dogecoin wallet is a great way to store your DOGE. A digital Dogecoin wallet allows you to keep your DOGE safely and securely, without having to worry about losing them or having them stolen.
Lesson 14: 5 Industries That Blockchain Will Disrupt in the Future
There’s no doubt that blockchain technology is changing the world. It has the potential to disrupt a wide range of industries, and we’re going to see more and more examples of this in the future. Here are five industries that we think will be particularly impacted by blockchain shortly:
– Healthcare
– Banking
– Food Safety
– Supply Chain Management
– Gaming
Lesson 15: Emerging Blockchain Applications Across Industries
Blockchain technology has been heavily disrupting the world of finance and other sectors for some time now. But this isn’t the only sector that is benefiting from this innovative technology. Here are some emerging blockchain applications that are having a big impact on industries across the board.
- Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used to track medical records more accurately and securely than ever before. It can also help decrease fraud by tracking medication prescriptions as they’re administered.
- Retail: Recent studies have shown that shoppers prefer items that have been authenticated using blockchain technology rather than traditional security measures, such as RFID tags or barcodes. This allows retailers to reduce costs associated with inventory management, theft prevention, and customer service issues.
- Logistics & Supply Chain Management
Lesson 16: How To Become a Blockchain Developer?
If you’re interested in developing on the blockchain, then it’s important to know how to become a blockchain developer. There are a few key steps that you need to take to get started:
- Learn about blockchains and cryptocurrencies.
- Understand coding principles and frameworks. This includes things like object-oriented programming (OOP), functional programming techniques, and data structures, such as stacks and queues.
- Get familiar with distributed systems design patterns.
- Incorporate security best practices into your development workflow from the very beginning.
Lesson 17: What is NFT?
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are a new kind of digital asset that offers unique benefits over other types of digital assets. Unlike regular cryptocurrencies, which are purely deflationary, NFTs can have a fixed supply and represent ownership of something tangible, such as virtual goods or intellectual property. This allows for more liquid markets and greater flexibility when it comes to exchanging them between users.
Lesson 18: The Complete Guide on Solidity Programming
Solidity is a language for programming smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. It is similar to other mainstream languages like Java and JavaScript, but it has been designed specifically for building decentralized applications.
Get Caltech CTME Circle Membership!
Caltech Blockchain BootcampExplore Program![]()
Lesson 19: The Future of Shiba Inu Coin?
Looking to invest in a crypto that has a bright future? Shiba Inu Coin may be the right choice for you! The idea is to create a global currency that is accessible to everyone, and that can be used to purchase goods and services. This innovative crypto is set to take the world of finance by storm in 2022, and there’s no telling how big it will become.
Lesson 20: Understanding the Fundamentals of Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic is a platform that runs on blockchain technology. It was created after the Ethereum network was attacked and compromised, resulting in the loss of millions of dollars worth of ERC20 tokens. Ethereum Classic aims to be the original Ethereum platform and offers several features that are unique to it.
Lesson 21: What is the Merkle Tree in Blockchain?
The Merkle Tree is a data structure used in blockchain technology. It helps to ensure the validity of transactions and builds a tamper-proof record of all events that have happened in the system. The tree consists of nodes or blocks, and each block contains a list of transaction hashes as well as other information (such as the time it was created).
Lesson 22: What is Cardano?
Cardano is a new blockchain platform that focuses on smart contracts, scalability, and decentralized applications. Cardano is designed to provide a solution for three major problems faced by current blockchains: high transaction fees, slow processing times, and lack of flexibility. Cardano uses a layered approach that allows it to scale up as needed without sacrificing functionality or decentralization. This allows it to handle high throughputs while still maintaining security guarantees.
Lesson 23: What is Matic Network?
Matic Network is a blockchain-based platform that allows businesses to hire dApps to power their operations. With Matic, companies can access the full range of features and capabilities offered by Ethereum while still keeping their data isolated from the public network.
Lesson 24: Top 30 Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers for 2022
Are you interested in learning more about blockchain? If so, we’ve got the perfect article for you. In this article, we will share with you the top 30 blockchain interview questions and answers for 2022. By knowing what is being asked, you will be able to show your skills and knowledge in the field and land your dream job.
Lesson 25: What is Tether?
Tether is a digital currency that operates on the Bitcoin blockchain. It was created in 2014 and is managed by Tether Limited, a company registered in the British Virgin Islands. Tether is used to purchase items in the real world, and its value is pegged to the value of the US dollar. Tether is backed by real-world assets, so it maintains its value even if the price of Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency falls.
Lesson 26: A Comprehensive Comparison Of NFT Vs. Crypto
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and cryptocurrencies are two of the most interesting new trends in blockchain technology.
- An NFT (non-fungible token) is a digital object that can have unique properties, such as ownership rights, scarcity levels, or functions.
- Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual units that use cryptography to secure their transactions and control the creation of new units.
Lesson 27: What Is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is a term used to describe the latest stage of the web development cycle. It refers to a new generation of web applications and services that are built using blockchain technology. At its core, Web 3.0 is about moving away from centralized control and embracing distributed ledgers. This shift will enable a more open and equitable web, where users can trust that their data is safe and their transactions are secure.
Earn a Caltech Badge on Your Resume!
Caltech Blockchain BootcampExplore Program![]()
Lesson 28: Types of Blockchain
There are a few different types of blockchain,
- Distributed ledger technology (DLT), also known as the blockchain, is a distributed database that maintains a continuously growing list of digital transactions. Transactions are spread across many nodes in the network, making it difficult for anyone to tamper with them. This makes it an excellent choice for cases where you need to track records that require transparency and trustworthiness, such as voting or contracts.
- A ConsenSys chain is similar to DLT in that every node keeps a copy of the data. However, unlike DLT, ConsenSys chains do not allow participants to add new entries without consensus from all other nodes in the network. This makes it useful for applications that require high security but low scalability (for example: tracking property rights).
- Smart contracts are code segments that run on Ethereum Virtual Machines and can be used to execute contractual obligations between parties automatically.
Lesson 29: What Is DeFi?
DeFi (distributed finance) is a term that refers to the use of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies to facilitate financial transactions. DeFi platforms allow users to make direct payments or borrow money using cryptocurrency as collateral. These platforms also provide access to a wide range of financial products, including loans, credit cards, and asset-backed securities.
Lesson 30: What Is Ripple?
Ripple is a cryptocurrency that can also be used to transfer money between different currencies. Ripple works by creating a global network of financial institutions that uses the Ripple ledger to make international payments easier and faster. This network allows banks and other organizations to send money directly to each other without having to go through traditional banking systems.
Lesson 31: What Is Binance?
Binance is a popular cryptocurrency exchange that offers users an easy and user-friendly platform to buy and sell cryptocurrencies. It has rapidly become one of the most popular exchanges in the world, with nearly two million registered users and over $1 billion in traded volume every day. Binance allows users to trade a variety of different digital assets, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and other altcoins.
Get Mentored by Leading Java Experts!
Full Stack Java DeveloperExplore Program![]()
Fuente
News
Terra Can’t Catch a Break as Blockchain Gets $6 Million Exploited

The attack, which exploited a vulnerability disclosed in April, drained around 60 million ASTRO tokens, sending the price plummeting.
The Terra blockchain has been exploited for over $6 million, forcing developers to take a momentary break the chain.
Beosin Cyber Security Company reported that the protocol lost 60 million ASTRO tokens, 3.5 million USDC, 500,000 USDT, and 2.7 BTC or $180,000.
Terra developers paused the chain on Wednesday morning to apply an emergency patch that would address the attack. Moments later, a 67% majority of validators upgraded their nodes and resumed block production.
The ASTRO token has plunged as much as 75%. It is now trading at $0.03, a 25% decline on the day. Traders who took advantage of the drop are now on 195%.
The vulnerability that took down the Cosmos-based blockchain was disclosed in April and involved the deployment of a malicious CosmWasm contract. It opened the door to attacks via what is called an “ibc-hooks callback timeout reentrancy vulnerability,” which is used to invoke contracts and enable cross-chain swaps.
Terra 2.0 also suffered a massive drop in total value locked (TVL) in April, shortly after the vulnerability was discovered. It plunged 80% to $6 million from $30 million in TVL and has since lost nearly half of that value, currently sitting at $3.9 million.
The current Earth chain emerged from the rubble as a hard fork after the original blockchain, now called Terra Classic, collapsed in 2022. Terra collapsed after its algorithmic stablecoin (UST) lost its peg, causing a run on deposits. More than $50 billion of UST’s market cap was wiped out in a matter of days.
Terraform Labs, the company behind the blockchain, has been slowly unravelling its legal woes since its mid-2022 crash. Founder Do Kwon awaits sentencing in Montenegro after he and his company were found liable for $40 billion in customer funds in early April.
On June 12, Terraform Labs settled with the SEC for $4.4 billion, for which the company will pay about $3.59 billion plus interest and a $420 million penalty. Meanwhile, Kwon will pay $204.3 million, including $110 million in restitution, interest and an $80 million penalty, a court filing showed.
News
Google and Coinbase Veterans Raise $5M to Build Icebreaker, Blockchain’s Answer to LinkedIn

Icebreaker: Think LinkedIn but on a Blockchain—announced Wednesday that it has secured $5 million in seed funding. CoinFund led the round, with participation from Accomplice, Anagram, and Legion Capital, among others.
The company, which is valued at $21 million, aims to become the world’s first open-source network for professional connections. Its co-founders, Dan Stone and Jack Dillé, come from Google AND Monetary base; Stone was a product manager at the cryptocurrency giant and also the co-creator of Google’s largest multi-identity measurement and marketing platform, while Dillé was a design manager for Google Working area.
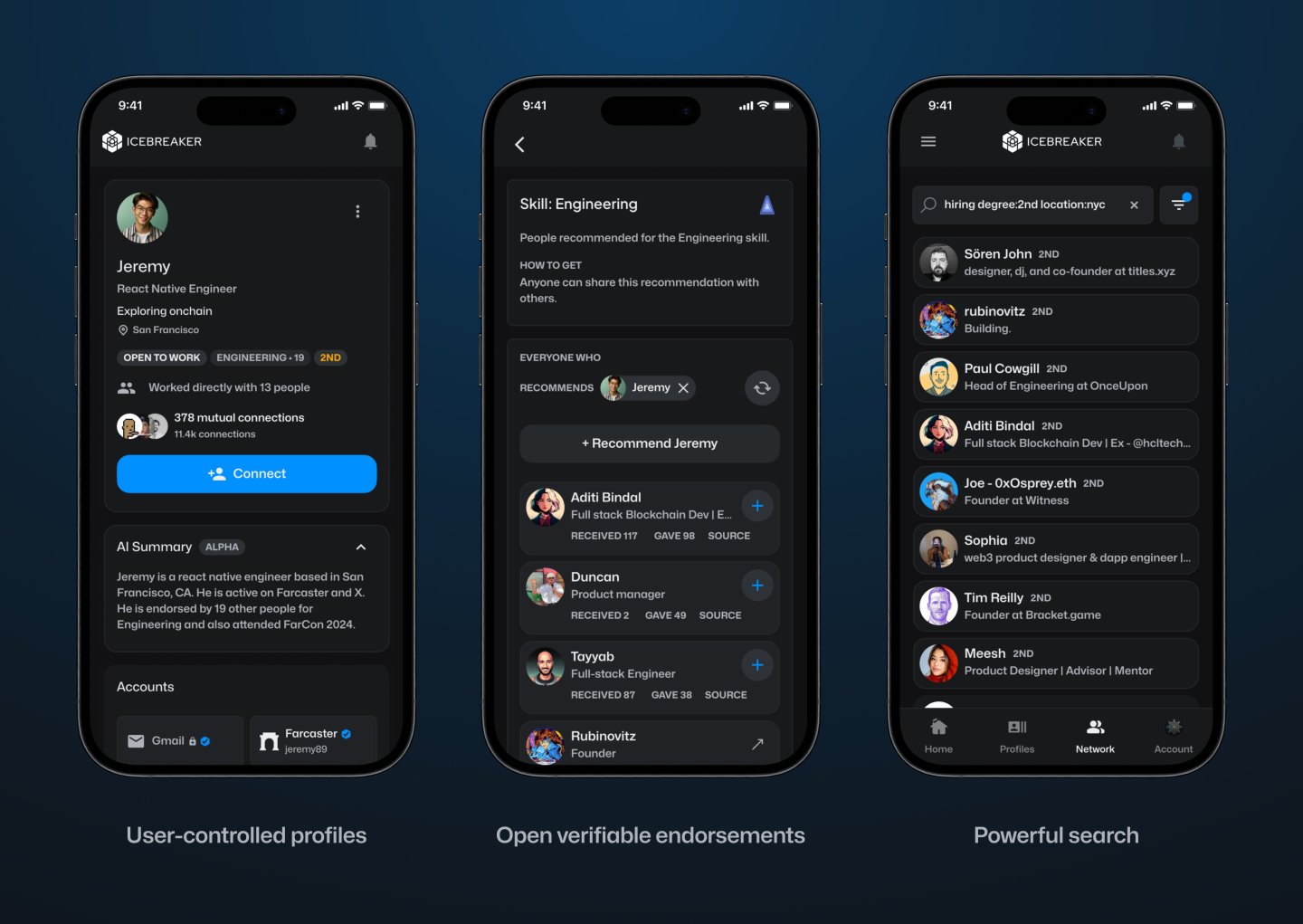
The pair founded Icebreaker on the shared belief that the imprint of one’s digital identity (and reputation) should not be owned by a single entity, but rather publicly owned and accessible to all. Frustrated that platforms like LinkedIn To limit how we leverage our connections, Dillé told Fortune he hopes to remove paywalls and credits, which “force us to pay just to browse our network.” Using blockchain technology, Icebreaker lets users transfer their existing professional profile and network into a single, verified channel.
“Imagine clicking the login button and then seeing your entire network on LinkedIn, ChirpingFarcaster and email? Imagine how many introductions could be routed more effectively if you could see the full picture of how you’re connected to someone,” Stone told Fortune.
Users can instantly prove their credentials and provide verifiable endorsements for people in their network. The idea is to create an “open graph of reputation and identity,” according to the founders. They hope to challenge LinkedIn’s closed network that “secures data,” freeing users to search for candidates and opportunities wherever they are online. By building on-chain, the founders note, they will create a public ledger of shared context and trust.
Verified channels are now launched for
Chirping
Online Guide
Wallet
Discord
Telephone
TeleporterYou can find them in Account -> Linked Accounts Italian: https://t.co/mRDyuWW8O2
— Icebreaker (@icebreaker_xyz) April 3, 2024
“Digital networking is increasingly saturated with noise and AI-driven fake personas,” the founders said in a statement. For example: Dillé’s LinkedIn headline reads “CEO of Google,” a small piece of digital performance art to draw attention to unverifiable information on Web2 social networks that can leave both candidates and recruiters vulnerable to false claims.
“Icebreaker was created to enable professionals to seamlessly tap into their existing profiles and networks to surface exceptional people and opportunities, using recent advances in cryptographically verifiable identity,” the company said, adding that the new funding will go towards expanding its team and developing products.
“One of the next significant use cases for cryptocurrency is the development of fundamental social graphs for applications to leverage… We are proud to support Dan, Jack and their team in their mission to bring true professional identity ownership to everyone online,” said CoinFund CIO Alex Felix in a statement.
Learn more about all things cryptocurrency with short, easy-to-read flashcards. Click here to Fortune’s Crash Course in Cryptocurrency.
Fuente
News
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
News
New bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work

The Department of Veterans Affairs would have to evaluate how blockchain technology could be used to improve benefits and services offered to veterans, according to a legislative proposal introduced Tuesday.
The bill, sponsored by Rep. Nancy Mace, R-S.C., would direct the VA to “conduct a comprehensive study of the feasibility, potential benefits, and risks associated with using distributed ledger technology in various programs and services.”
Distributed ledger technology, including blockchain, is used to protect and track information by storing data across multiple computers and keeping a record of its use.
According to the text of the legislation, which Mace’s office shared exclusively with Nextgov/FCW ahead of its publication, blockchain “could significantly improve benefits allocation, insurance program management, and recordkeeping within the Department of Veterans Affairs.”
“We need to bring the federal government into the 21st century,” Mace said in a statement. “This bill will open the door to research on improving outdated systems that fail our veterans because we owe it to them to use every tool at our disposal to improve their lives.”
Within one year of the law taking effect, the Department of Veterans Affairs will be required to submit a report to the House and Senate Veterans Affairs committees detailing its findings, as well as the benefits and risks identified in using the technology.
The mandatory review is expected to include information on how the department’s use of blockchain could improve the way benefits decisions are administered, improve the management and security of veterans’ personal data, streamline the insurance claims process, and “increase transparency and accountability in service delivery.”
The Department of Veterans Affairs has been studying the potential benefits of using distributed ledger technology, with the department emission a request for information in November 2021 seeking input from contractors on how blockchain could be leveraged, in part, to streamline its supply chains and “secure data sharing between institutions.”
The VA’s National Institute of Artificial Intelligence has also valued the use of blockchain, with three of the use cases tested during the 2021 AI tech sprint focused on examining its capabilities.
Mace previously introduced a May bill that would direct Customs and Border Protection to create a public blockchain platform to store and share data collected at U.S. borders.
Lawmakers also proposed additional measures that would push the Department of Veterans Affairs to consider adopting other modernized technologies to improve veteran services.
Rep. David Valadao, R-Calif., introduced legislation in June that would have directed the department to report to lawmakers on how it plans to expand the use of “certain automation tools” to process veterans’ claims. The House of Representatives Subcommittee on Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs gave a favorable hearing on the congressman’s bill during a Markup of July 23.
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin, ETH Price, CPI Print, PYTH, WIF & MORE!!
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin Price, ETF, ETH, WIF, HNT & MORE!!
-

 DeFi9 months ago
DeFi9 months agoMetasphere Labs announces follow-up event regarding
-
 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoSolana price potential?! Check out THIS update if you own SOL!!
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoWho Really CONTROLS THE MARKETS!! Her plans REVEALED!!
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoPump.Fun Overtakes Ethereum in Daily Revenue: A New Leader in DeFi
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoNew bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoDegens Can Now Create Memecoins From Tweets
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoLawmakers, regulators to study impact of blockchain and cryptocurrency in Alabama • Alabama Reflector
-

 Bitcoin6 months ago
Bitcoin6 months ago1 Top Cryptocurrency That Could Surge Over 4,300%, According to This Wall Street Firm
-

 Ethereum8 months ago
Ethereum8 months agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoCryptocurrency News: BTC Rally, ETH, SOL, FTM, USDT Recover & MORE!

 ASTRO Price
ASTRO Price



