News
OODA Loop – The National Blockchain Standard… in China

In June 2023, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced “a national standard for blockchain technology to guide the development of the industry.” In this post: an analysis of the strategic policy initiatives in the lead-up to the June 2023 unveiling of the Chinese national blockchain standard – and future scenarios.
The History of Blockchain in China
The history of blockchain in China is a fascinating journey that reflects the country’s strategic approach to technology and innovation. China’s engagement with blockchain technology began in earnest around the early 2010s, paralleling global interest but with distinct characteristics reflective of its centralized governance and strategic economic priorities.
Initially, China, like many other countries, was intrigued by the potential of cryptocurrencies. However, the Chinese government quickly distinguished between cryptocurrencies and the underlying blockchain technology, embracing the latter while imposing strict regulations on the former. This was evident from the early bans on cryptocurrency exchanges and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) in 2017, which aimed to curb financial risk and speculative trading that could destabilize the economy.
Despite these restrictions on cryptocurrencies, the Chinese government recognized the transformative potential of blockchain technology itself. This led to significant state-sponsored initiatives to integrate blockchain into various sectors of the economy. For instance, in sectors like supply chain management, financial services, and even governmental operations, blockchain was seen as a tool to enhance efficiency, transparency, and trust.
A pivotal moment in the history of blockchain in China was the endorsement of the technology by President Xi Jinping in 2019, where he highlighted blockchain as a critical part of the new industrial transformation. This endorsement was not merely rhetorical but was followed by substantial policy support and investments. For example, major cities like Shanghai and Beijing announced significant funds to support blockchain projects and startups.
Moreover, the development of the Blockchain-based Service Network (BSN) in 2020 marked a significant step in China’s blockchain strategy. The BSN is intended to be a global infrastructure to help developers create and manage blockchain applications more cheaply and efficiently. This initiative is particularly noteworthy as it aligns with China’s ambition to set global standards in emerging technologies and reflects its approach to using state-led infrastructure to shape technological ecosystems.
In recent years, the focus has also been on integrating blockchain technology with other strategic technologies like artificial intelligence and 5G, further embedding it into the national strategy of technological supremacy. This integration is seen as a way to enhance the capabilities of these technologies and to develop new forms of applications that are secure, reliable, and scalable.
China’s approach to blockchain, characterized by strong governmental support and strategic integration into national economic and technological policies, contrasts with more market-driven approaches in other parts of the world. This has allowed China to not only lead in certain aspects of blockchain technology development but also to attempt to define the frameworks and standards around its use, both domestically and globally.
Recent Policy and Strategy Background
Coindesk provided coverage of the strategic policy initiatives in the lead-up to the June 2023 unveiling of the Chinese national blockchain standard:
June 2021
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology Outlines Proposals for Blockchain Development
China should “promote the deep integration of blockchain and economy and society and accelerate the promotion of blockchain technology for application and industrial development.”
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has outlined its proposals to accelerate the application and development of blockchain technology across the country’s economy and elsewhere. The MIIT has put forward its proposals in accordance with President Xi Jinping’s “Socialism With Chinese Characteristics for a New Era“. China should “promote the deep integration of blockchain and economy and society and accelerate the promotion of blockchain technology for application and industrial development,” according to a document written on May 27 and published Monday.
The MIIT suggested that blockchain could enhance the real economy by improving supply chain management, product traceability, data sharing, and more. However, blockchain would also be used to improve the collection of data for the purposes of judicial deposit, real estate registration and law enforcement. China’s development of a central bank digital currency (CBDC) is well known, with its digital yuan, or eCNY, currently being piloted in numerous cities. The proposals published by the MIIT also reveal the extent to which the CCP believes blockchain itself can be applied to the development of its country’s economy.
October 2021
China to Release National Blockchain Standard Next Year, Says Official: Report
While cracking down on the cryptocurrency industry, Beijing is pouring resources into blockchain for governmental and enterprise use.
China’s technology standardization body will issue a national standard for blockchain next year, said an official from the China Electronics Standardization Institute, according to news site Chuanguan.
-
The institute has drafted a standard and is in the process of approving it, said Li Ming, director of the Blockchain Research Office at the standardization body, during the Fifth China Blockchain Development Competition held in Chengdu, Sichuan.
- China is looking to boost blockchain innovation and application in enterprise and government across the country even as it clamps down on crypto. Its latest Five-Year Plan, a planning document that outlines development goals, put blockchain on a par with artificial intelligence, big data and cloud computing.
-
Li said that standards are fundamental to an industry and used the example of Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Without a unified standard, he said, devices from different manufacturers wouldn’t be able to connect to the network.
-
Once the standard is set, the body will look into drafting evaluation criteria around it so that a “benign” ecosystem can be created, the director said.
- Key government projects like the Blockchain Services Network and Xinghuo Chain follow an “open permissioned” protocol, which seeks to retain some of the benefits of decentralization while maintaining centralized control.
-
Exporting Chinese-made blockchain and standards is also a goal of these projects.
- Last year, the International Telecommunications Union passed a set of blockchain standards for financial applications developed by the People’s Bank of China, the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, and Huawei.
-
The institute is responsible for drafting tech standards and is under China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
-
Chuanguan is a site operated by Sichuan Daily, a state-run newspaper in China’s southwestern province.
January 2023
China Launches Smart-Contract Functionality on Digital Yuan Through E-Commerce App Meituan
Through the smart contract, users can win part of a daily prize of $1,312 for using the digital yuan.
China has enabled smart-contract functionality for its central bank digital currency (CBDC), the digital yuan, through the e-commerce app Meituan, one of China’s largest food delivery and lifestyle apps. China has been at the forefront of CBDC development among major countries, as it started to test the digital currency as early as 2020. The currency has been used in retail transactions and to buy securities, but smart-contract functionality on a mass retail scale has yet to be tested.
At the end of 2022, digital yuan accounted for 0.13% of the total circulation of Chinese renminbi yuan, the People’s Bank of China said earlier in January. The PBOC’s Digital Currency Institute said in September it was working to increase smart-contract functionality and later rolled out a smart contract-based function that prevents payees from wrongfully taking prepaid funds.
February 2023
China Targets Blockchain Breakthroughs With Beijing Research Center: Report
The center will focus on blockchain use related to the economy and individuals’ livelihoods in an attempt to make the technology central to China’s digital infrastructure.
China is establishing a blockchain research center in Beijing as it explores integrating the technology more extensively into day-to-day life, the South China Morning Post reported on Thursday. The Ministry of Science and Technology approved the establishment of the National Blockchain Technology Innovation Center recently, the SCMP reported, citing the government-run newspaper Beijing Daily. The center will focus on major use cases related to the economy and individuals’ livelihoods in an attempt to make blockchain central to China’s digital infrastructure.
The move reflects the government’s enthusiasm for the technology despite having banned the use of cryptocurrency. Blockchain received its first mention in China’s most recent five-year policy plan in 2021, which said it would play a key role in the country’s digital economy. As of July [2023], more than 1,800 blockchain companies were registered with the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC), the SCMP reported.
The Chinese National Blockchain Standard
June 2023
China publishes national blockchain standard
China has released standardized guidelines for the blockchain industry to boost its rapid growth and adoption in the country.
China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has published a national standard for blockchain technology to guide the development of the industry in the country, a state-run news channel CGTN reported on June 2 [2023]
The guideline reportedly standardizes the blockchain system’s functional architecture and core elements, serving as a reference to better understand and utilize the emerging technology. MIIT reportedly stated that the standard aims to accelerate the standardization of China’s blockchain industry and drive its further development. Global Times reported that over a hundred blockchain companies in the country have been applying the standard to their operations.
China is pro-blockchain technology
Despite China’s strict anti-crypto stance, the Asian country has actively explored the use of blockchain technology. In September 2022, a Chinese government official said the country accounts for 84% of all blockchain applications filed worldwide.
On May 10, China launched a new national blockchain research center designed to connect universities, developers, and blockchain businesses, fostering the industry’s growth. This center is tasked with developing research and innovations that can further China’s expansion into the blockchain space.
The Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission recently published a white paper covering various technologies, such as blockchain and AI. The white paper emphasizes a commitment to web3 and metaverse innovations and plans to become an industry leader by 2025.
Several crypto community members, including Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao, noted that the white paper’s timing signaled the beginning of a more open approach to digital assets.
China has also leveraged blockchain technology to make significant progress in developing its digital yuan CBDC. The national digital currency has been trialed in several jurisdictions and has enjoyed some success since its development began.
What Next?
The release of a national standard for blockchain technology by China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) is a significant development in the global deployment of blockchain. This initiative is part of China’s broader strategy to become a leader in the technological innovations that will drive future economies, while also setting standards that could potentially become global benchmarks.
Historically, China has taken a dual approach to blockchain technology. On one hand, it has been very cautious with cryptocurrencies, imposing strict regulations to curb speculative trading and financial risks associated with them. On the other hand, it has been very supportive of blockchain technology itself, recognizing its potential to enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in various sectors.
The national standard released by the MIIT is intended to guide the development of the blockchain industry in China by establishing clear guidelines and frameworks for the technology’s application. This includes technical standards, business and industry standards, and even ethical standards to ensure that blockchain technology is used in a way that is secure, reliable, and beneficial to societal needs.
This move is strategic for several reasons:
- Innovation and Leadership: By setting national standards, China positions itself as a leader in blockchain technology, encouraging innovation and setting benchmarks that could influence global practices.
- Regulatory Clarity: Clear standards help in providing regulatory clarity for companies and developers, which is essential for fostering investment and innovation in the blockchain space.
- Global Influence: As blockchain technology continues to evolve, having a set of standards could help Chinese companies export their technology and practices abroad, influencing how blockchain is implemented worldwide.
The implications of this initiative are profound. It not only underscores China’s commitment to leading in high-tech industries but also highlights the importance of regulatory frameworks in fostering technological advancements. The release of these standards could accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology in various sectors, from finance to supply chain management, both within China and globally.
Further OODA Loop Scenarios
China’s move to implement a national standard for blockchain technology is a strategic maneuver that could significantly alter the global technological landscape. By establishing these standards, China is not merely influencing the blockchain sector within its borders but is also positioning itself as a pivotal player in the global arena. Here are several scenarios that could unfold as China pursues this path:
- Global Standard Setter: One of the most direct impacts of China’s national blockchain standards could be their adoption internationally. If Chinese companies can leverage these standards to enhance the interoperability and efficiency of their blockchain solutions, these standards could become attractive to other nations, especially those in the developing world that may not have the infrastructure to develop their own. This could lead to a scenario where China’s standards become de facto global norms.
- Innovation Hub: With clear standards in place, China could attract a significant amount of blockchain-related research and development. Companies and startups might find a more predictable regulatory and technological environment appealing, leading to an innovation boom. This could be similar to the surge in blockchain investments seen in recent years, where the technology’s potential catalyzed a wave of innovation and investment.
- Enhanced Export Capabilities: The adoption of national standards could streamline the process for Chinese blockchain companies to export their technology and services. This standardization could reduce the complexity and cost of deploying these solutions internationally, giving Chinese companies a competitive edge in global markets.
- Strategic Industries: Blockchain technology could be integrated into critical areas such as manufacturing, supply chain logistics, and even governance, aligning with China’s broader goals of upgrading its industrial base and improving administrative efficiency. This could enhance productivity and transparency, propelling economic growth and reinforcing China’s strategic competitive advantage.
- Digital Sovereignty: By setting its own standards, China could further its goals of digital sovereignty, reducing its dependence on Western technology standards and asserting more control over its digital economy. This could lead to a more bifurcated global technology landscape, where different blocs use different technology standards, echoing the broader geopolitical tensions between China and the West.
These scenarios are not without challenges. The global acceptance of Chinese standards could be hindered by geopolitical tensions, especially with countries wary of China’s technological ascendancy and its implications for security and privacy. Additionally, the success of this initiative depends on the Chinese government’s ability to foster innovation while maintaining tight regulatory controls, a balance that has historically been difficult to achieve.
What potential challenges do you foresee for China in achieving global technological and strategic competitive advantage through the implementation of a national standard for blockchain technology?
NOTE: This OODA Loop Original Analysis was partially generated with the cognitive augmentation of and in collaboration with ALTzero Project – MattGPT.
Additional OODA Loop Resources
For our News Briefs and Original Analysis research efforts to date on this topic, go to:
OODA Loop | Blockchain OODA Loop | Trust OODA Loop | Zero Trust OODA Loop | Trustworthy AI
The OODA Loop Digital Self-Sovereignty Research Initiative: Digital self-sovereignty is the new “build” as legacy systems get swapped out in a sometimes violent, always exponential fashion. To be clear, we are positioning digital self-sovereignty as a solution to our current problem set that will “still stand” even if this current geopolitical, exponential technology-driven inflection point manifests – for a prolonged period – as dark age-esque global societal systemic failure (per The Ministry of the Future). Ironically, this same uncertainty, chaos, and violence are the primary drivers (and new incentive structure) behind this new system’s development. In this post, we “set levels” and offer working definitions for our forthcoming Q324 (going right into OODAcon 2024) series of posts as part of our Digital Self-Sovereignty Research Initiative.
Embracing Corporate Intelligence and Scenario Planning in an Uncertain Age: Businesses also confront unpredictable external threats besides traditional competitive challenges. This environment amplifies the significance of Scenario Planning. It enables leaders to envision varied futures, thereby identifying potential risks and opportunities. Regardless of size, all organizations should allocate time to refine their understanding of the current risk landscape and adapt their strategies. See: Scenario Planning
Bitcoin’s Momentum: Bitcoin seems unstoppable due to solid mathematical foundations and widespread societal acceptance. Other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum also gain prominence. The Metaverse’s rise is closely tied to Ethereum’s universal trust layer. See: Guide to Crypto Revolution
Geopolitical-Cyber Risk Nexus: The interconnectivity brought by the Internet has made regional issues affect global cyberspace. Now, every significant event has cyber implications, making it imperative for leaders to recognize and act upon the symbiosis between geopolitical and cyber risks. See The Cyber Threat
Track Technology Driven Disruption: Businesses should examine technological drivers and future customer demands. A multi-disciplinary knowledge of tech domains is essential for effective foresight. See: Disruptive and Exponential Technologies.
Networked Extremism: The digital era enables extremists worldwide to collaborate, share strategies, and self-radicalize. Meanwhile, advanced technologies empower criminals, making corruption and crime interwoven challenges for global societies. See: Converging Insurgency, Crime and Corruption
News
Terra Can’t Catch a Break as Blockchain Gets $6 Million Exploited

The attack, which exploited a vulnerability disclosed in April, drained around 60 million ASTRO tokens, sending the price plummeting.
The Terra blockchain has been exploited for over $6 million, forcing developers to take a momentary break the chain.
Beosin Cyber Security Company reported that the protocol lost 60 million ASTRO tokens, 3.5 million USDC, 500,000 USDT, and 2.7 BTC or $180,000.
Terra developers paused the chain on Wednesday morning to apply an emergency patch that would address the attack. Moments later, a 67% majority of validators upgraded their nodes and resumed block production.
The ASTRO token has plunged as much as 75%. It is now trading at $0.03, a 25% decline on the day. Traders who took advantage of the drop are now on 195%.
The vulnerability that took down the Cosmos-based blockchain was disclosed in April and involved the deployment of a malicious CosmWasm contract. It opened the door to attacks via what is called an “ibc-hooks callback timeout reentrancy vulnerability,” which is used to invoke contracts and enable cross-chain swaps.
Terra 2.0 also suffered a massive drop in total value locked (TVL) in April, shortly after the vulnerability was discovered. It plunged 80% to $6 million from $30 million in TVL and has since lost nearly half of that value, currently sitting at $3.9 million.
The current Earth chain emerged from the rubble as a hard fork after the original blockchain, now called Terra Classic, collapsed in 2022. Terra collapsed after its algorithmic stablecoin (UST) lost its peg, causing a run on deposits. More than $50 billion of UST’s market cap was wiped out in a matter of days.
Terraform Labs, the company behind the blockchain, has been slowly unravelling its legal woes since its mid-2022 crash. Founder Do Kwon awaits sentencing in Montenegro after he and his company were found liable for $40 billion in customer funds in early April.
On June 12, Terraform Labs settled with the SEC for $4.4 billion, for which the company will pay about $3.59 billion plus interest and a $420 million penalty. Meanwhile, Kwon will pay $204.3 million, including $110 million in restitution, interest and an $80 million penalty, a court filing showed.
News
Google and Coinbase Veterans Raise $5M to Build Icebreaker, Blockchain’s Answer to LinkedIn

Icebreaker: Think LinkedIn but on a Blockchain—announced Wednesday that it has secured $5 million in seed funding. CoinFund led the round, with participation from Accomplice, Anagram, and Legion Capital, among others.
The company, which is valued at $21 million, aims to become the world’s first open-source network for professional connections. Its co-founders, Dan Stone and Jack Dillé, come from Google AND Monetary base; Stone was a product manager at the cryptocurrency giant and also the co-creator of Google’s largest multi-identity measurement and marketing platform, while Dillé was a design manager for Google Working area.
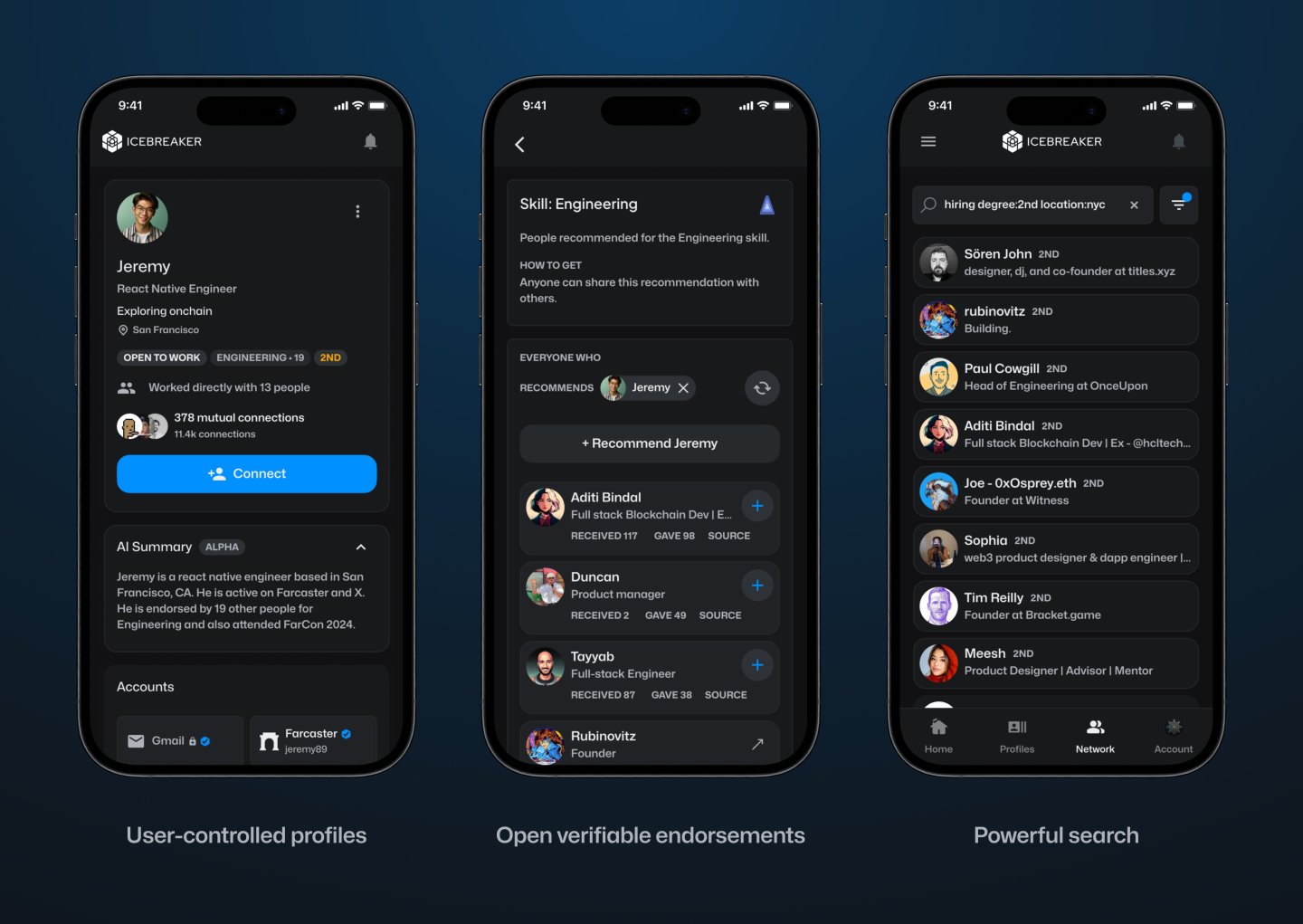
The pair founded Icebreaker on the shared belief that the imprint of one’s digital identity (and reputation) should not be owned by a single entity, but rather publicly owned and accessible to all. Frustrated that platforms like LinkedIn To limit how we leverage our connections, Dillé told Fortune he hopes to remove paywalls and credits, which “force us to pay just to browse our network.” Using blockchain technology, Icebreaker lets users transfer their existing professional profile and network into a single, verified channel.
“Imagine clicking the login button and then seeing your entire network on LinkedIn, ChirpingFarcaster and email? Imagine how many introductions could be routed more effectively if you could see the full picture of how you’re connected to someone,” Stone told Fortune.
Users can instantly prove their credentials and provide verifiable endorsements for people in their network. The idea is to create an “open graph of reputation and identity,” according to the founders. They hope to challenge LinkedIn’s closed network that “secures data,” freeing users to search for candidates and opportunities wherever they are online. By building on-chain, the founders note, they will create a public ledger of shared context and trust.
Verified channels are now launched for
Chirping
Online Guide
Wallet
Discord
Telephone
TeleporterYou can find them in Account -> Linked Accounts Italian: https://t.co/mRDyuWW8O2
— Icebreaker (@icebreaker_xyz) April 3, 2024
“Digital networking is increasingly saturated with noise and AI-driven fake personas,” the founders said in a statement. For example: Dillé’s LinkedIn headline reads “CEO of Google,” a small piece of digital performance art to draw attention to unverifiable information on Web2 social networks that can leave both candidates and recruiters vulnerable to false claims.
“Icebreaker was created to enable professionals to seamlessly tap into their existing profiles and networks to surface exceptional people and opportunities, using recent advances in cryptographically verifiable identity,” the company said, adding that the new funding will go towards expanding its team and developing products.
“One of the next significant use cases for cryptocurrency is the development of fundamental social graphs for applications to leverage… We are proud to support Dan, Jack and their team in their mission to bring true professional identity ownership to everyone online,” said CoinFund CIO Alex Felix in a statement.
Learn more about all things cryptocurrency with short, easy-to-read flashcards. Click here to Fortune’s Crash Course in Cryptocurrency.
Fuente
News
Luxembourg proposes updates to blockchain laws | Insights and resources

On July 24, 2024, the Ministry of Finance proposed Blockchain Bill IVwhich will provide greater flexibility and legal certainty for issuers using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). The bill will update three of Luxembourg’s financial laws, the Law of 6 April 2013 on dematerialised securitiesTHE Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 23 December 1998 establishing a financial sector supervisory commissionThis bill includes the additional option of a supervisory agent role and the inclusion of equity securities in dematerialized form.
DLT and Luxembourg
DLT is increasingly used in the financial and fund management sector in Luxembourg, offering numerous benefits and transforming various aspects of the industry.
Here are some examples:
- Digital Bonds: Luxembourg has seen multiple digital bond issuances via DLT. For example, the European Investment Bank has issued bonds that are registered, transferred and stored via DLT processes. These bonds are governed by Luxembourg law and registered on proprietary DLT platforms.
- Fund Administration: DLT can streamline fund administration processes, offering new opportunities and efficiencies for intermediaries, and can do the following:
- Automate capital calls and distributions using smart contracts,
- Simplify audits and ensure reporting accuracy through transparent and immutable transaction records.
- Warranty Management: Luxembourg-based DLT platforms allow clients to swap ownership of baskets of securities between different collateral pools at precise times.
- Tokenization: DLT is used to tokenize various assets, including real estate and luxury goods, by representing them in a tokenized and fractionalized format on the blockchain. This process can improve the liquidity and accessibility of traditionally illiquid assets.
- Tokenization of investment funds: DLT is being explored for the tokenization of investment funds, which can streamline the supply chain, reduce costs, and enable faster transactions. DLT can automate various elements of the supply chain, reducing the need for reconciliations between entities such as custodians, administrators, and investment managers.
- Issuance, settlement and payment platforms:Market participants are developing trusted networks using DLT technology to serve as a single source of shared truth among participants in financial instrument investment ecosystems.
- Legal framework: Luxembourg has adapted its legal framework to accommodate DLT, recognising the validity and enforceability of DLT-based financial instruments. This includes the following:
- Allow the use of DLT for the issuance of dematerialized securities,
- Recognize DLT for the circulation of securities,
- Enabling financial collateral arrangements on DLT financial instruments.
- Regulatory compliance: DLT can improve transparency in fund share ownership and regulatory compliance, providing fund managers with new opportunities for liquidity management and operational efficiency.
- Financial inclusion: By leveraging DLT, Luxembourg aims to promote greater financial inclusion and participation, potentially creating a more diverse and resilient financial system.
- Governance and ethics:The implementation of DLT can promote higher standards of governance and ethics, contributing to a more sustainable and responsible financial sector.
Luxembourg’s approach to DLT in finance and fund management is characterised by a principle of technology neutrality, recognising that innovative processes and technologies can contribute to improving financial services. This is exemplified by its commitment to creating a compatible legal and regulatory framework.
Short story
Luxembourg has already enacted three major blockchain-related laws, often referred to as Blockchain I, II and III.
Blockchain Law I (2019): This law, passed on March 1, 2019, was one of the first in the EU to recognize blockchain as equivalent to traditional transactions. It allowed the use of DLT for account registration, transfer, and materialization of securities.
Blockchain Law II (2021): Enacted on 22 January 2021, this law strengthened the Luxembourg legal framework on dematerialised securities. It recognised the possibility of using secure electronic registration mechanisms to issue such securities and expanded access for all credit institutions and investment firms.
Blockchain Act III (2023): Also known as Bill 8055, this is the most recent law in the blockchain field and was passed on March 14, 2023. This law has integrated the Luxembourg DLT framework in the following way:
- Update of the Act of 5 August 2005 on provisions relating to financial collateral to enable the use of electronic DLT as collateral on financial instruments registered in securities accounts,
- Implementation of EU Regulation 2022/858 on a pilot scheme for DLT-based market infrastructures (DLT Pilot Regulation),
- Redefining the notion of financial instruments in Law of 5 April 1993 on the financial sector and the Law of 30 May 2018 on financial instruments markets to align with the corresponding European regulations, including MiFID.
The Blockchain III Act strengthened the collateral rules for digital assets and aimed to increase legal certainty by allowing securities accounts on DLT to be pledged, while maintaining the efficient system of the 2005 Act on Financial Collateral Arrangements.
With the Blockchain IV bill, Luxembourg will build on the foundations laid by previous Blockchain laws and aims to consolidate Luxembourg’s position as a leading hub for financial innovation in Europe.
Blockchain Bill IV
The key provisions of the Blockchain IV bill include the following:
- Expanded scope: The bill expands the Luxembourg DLT legal framework to include equity securities in addition to debt securities. This expansion will allow the fund industry and transfer agents to use DLT to manage registers of shares and units, as well as to process fund shares.
- New role of the control agent: The bill introduces the role of a control agent as an alternative to the central account custodian for the issuance of dematerialised securities via DLT. This control agent can be an EU investment firm or a credit institution chosen by the issuer. This new role does not replace the current central account custodian, but, like all other roles, it must be notified to the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier (CSSF), which is designated as the competent supervisory authority. The notification must be submitted two months after the control agent starts its activities.
- Responsibilities of the control agent: The control agent will manage the securities issuance account, verify the consistency between the securities issued and those registered on the DLT network, and supervise the chain of custody of the securities at the account holder and investor level.
- Simplified payment processesThe bill allows issuers to meet payment obligations under securities (such as interest, dividends or repayments) as soon as they have paid the relevant amounts to the paying agent, settlement agent or central account custodian.
- Simplified issuance and reconciliationThe bill simplifies the process of issuing, holding and reconciling dematerialized securities through DLT, eliminating the need for a central custodian to have a second level of custody and allowing securities to be credited directly to the accounts of investors or their delegates.
- Smart Contract Integration:The new processes can be executed using smart contracts with the assistance of the control agent, potentially increasing efficiency and reducing intermediation.
These changes are expected to bring several benefits to the Luxembourg financial sector, including:
- Fund Operations: Greater efficiency and reduced costs by leveraging DLT for the issuance and transfer of fund shares.
- Financial transactions: Greater transparency and security.
- Transparency of the regulatory environment: Increased attractiveness and competitiveness of the Luxembourg financial centre through greater legal clarity and flexibility for issuers and investors using DLT.
- Smart Contracts: Potential for automation of contractual terms, reduction of intermediaries and improvement of transaction traceability through smart contracts.
Blockchain Bill IV is part of Luxembourg’s ongoing strategy to develop a strong digital ecosystem as part of its economy and maintain its status as a leading hub for financial innovation. Luxembourg is positioning itself at the forefront of Europe’s growing digital financial landscape by constantly updating its regulatory framework.
Local regulations, such as Luxembourg law, complement European regulations by providing a more specific legal framework, adapted to local specificities. These local laws, together with European initiatives, aim to improve both the use and the security of projects involving new technologies. They help establish clear standards and promote consumer trust, while promoting innovation and ensuring better protection against potential risks associated with these emerging technologies. Check out our latest posts on these topics and, for more information on this law, blockchain technology and the tokenization mechanism, do not hesitate to contact us.
We are available to discuss any project related to digital finance, cryptocurrencies and disruptive technologies.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethics rules of some jurisdictions, is provided with the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal or other professional advice by Goodwin or its attorneys. Past results do not guarantee a similar outcome.
News
New bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work

The Department of Veterans Affairs would have to evaluate how blockchain technology could be used to improve benefits and services offered to veterans, according to a legislative proposal introduced Tuesday.
The bill, sponsored by Rep. Nancy Mace, R-S.C., would direct the VA to “conduct a comprehensive study of the feasibility, potential benefits, and risks associated with using distributed ledger technology in various programs and services.”
Distributed ledger technology, including blockchain, is used to protect and track information by storing data across multiple computers and keeping a record of its use.
According to the text of the legislation, which Mace’s office shared exclusively with Nextgov/FCW ahead of its publication, blockchain “could significantly improve benefits allocation, insurance program management, and recordkeeping within the Department of Veterans Affairs.”
“We need to bring the federal government into the 21st century,” Mace said in a statement. “This bill will open the door to research on improving outdated systems that fail our veterans because we owe it to them to use every tool at our disposal to improve their lives.”
Within one year of the law taking effect, the Department of Veterans Affairs will be required to submit a report to the House and Senate Veterans Affairs committees detailing its findings, as well as the benefits and risks identified in using the technology.
The mandatory review is expected to include information on how the department’s use of blockchain could improve the way benefits decisions are administered, improve the management and security of veterans’ personal data, streamline the insurance claims process, and “increase transparency and accountability in service delivery.”
The Department of Veterans Affairs has been studying the potential benefits of using distributed ledger technology, with the department emission a request for information in November 2021 seeking input from contractors on how blockchain could be leveraged, in part, to streamline its supply chains and “secure data sharing between institutions.”
The VA’s National Institute of Artificial Intelligence has also valued the use of blockchain, with three of the use cases tested during the 2021 AI tech sprint focused on examining its capabilities.
Mace previously introduced a May bill that would direct Customs and Border Protection to create a public blockchain platform to store and share data collected at U.S. borders.
Lawmakers also proposed additional measures that would push the Department of Veterans Affairs to consider adopting other modernized technologies to improve veteran services.
Rep. David Valadao, R-Calif., introduced legislation in June that would have directed the department to report to lawmakers on how it plans to expand the use of “certain automation tools” to process veterans’ claims. The House of Representatives Subcommittee on Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs gave a favorable hearing on the congressman’s bill during a Markup of July 23.
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin, ETH Price, CPI Print, PYTH, WIF & MORE!!
-

 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoCrypto News: Bitcoin Price, ETF, ETH, WIF, HNT & MORE!!
-

 DeFi9 months ago
DeFi9 months agoMetasphere Labs announces follow-up event regarding
-
 Videos9 months ago
Videos9 months agoSolana price potential?! Check out THIS update if you own SOL!!
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoWho Really CONTROLS THE MARKETS!! Her plans REVEALED!!
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoPump.Fun Overtakes Ethereum in Daily Revenue: A New Leader in DeFi
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoNew bill pushes Department of Veterans Affairs to examine how blockchain can improve its work
-

 DeFi6 months ago
DeFi6 months agoDegens Can Now Create Memecoins From Tweets
-

 News6 months ago
News6 months agoLawmakers, regulators to study impact of blockchain and cryptocurrency in Alabama • Alabama Reflector
-

 Bitcoin6 months ago
Bitcoin6 months ago1 Top Cryptocurrency That Could Surge Over 4,300%, According to This Wall Street Firm
-

 Ethereum8 months ago
Ethereum8 months agoComment deux frères auraient dérobé 25 millions de dollars lors d’un braquage d’Ethereum de 12 secondes • The Register
-

 Videos8 months ago
Videos8 months agoCryptocurrency News: BTC Rally, ETH, SOL, FTM, USDT Recover & MORE!













 ASTRO Price
ASTRO Price


